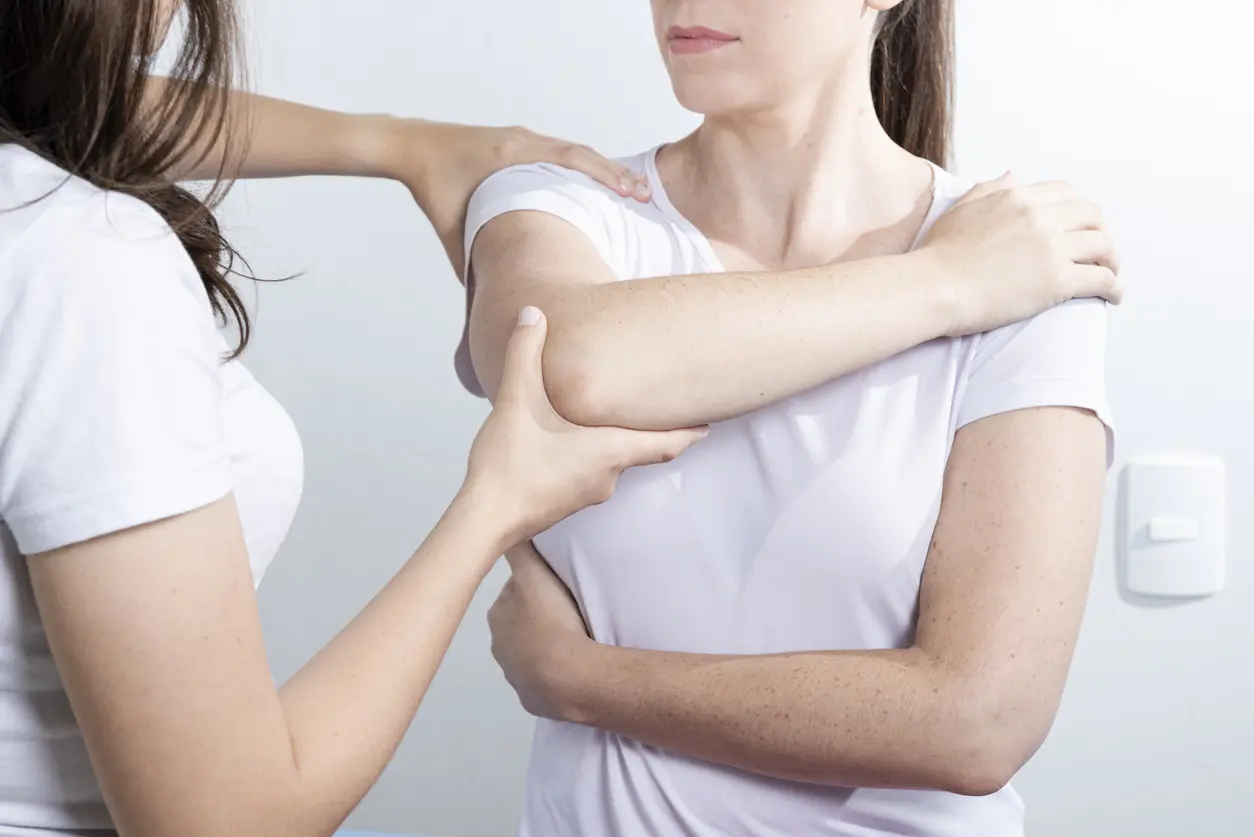
What Causes Right Arm Pain?
Right arm pain can result from muscle injuries, overuse, poor circulation, pinched nerves, or underlying conditions like arthritis or even heart disease. Severity and location of the pain help determine the cause.
Why You Might Have Right Arm Pain (Causes and Risks)
Have you ever experienced pain in your right arm? There's no need to feel alone if this is the case. Every year, millions of people suffer from right arm pain. Our arm muscles, joints, and tendons are susceptible to injury or pain.
Overuse injuries, accidents, and underlying medical conditions can all cause right arm pain.
Depending on the cause of the right arm pain, treatment will vary. In some cases, you may only need rest and home remedies to ease your pain. Medical treatment may be necessary in other cases.
This blog post explores some causes and treatment options for right arm pain. Additionally, we'll discuss some ways to prevent right arm pain. Read on if you're experiencing right arm pain! Here, you'll find the information you need to feel better.
What Right Arm Pain Means and Common Triggers
Right arm pain refers to any pain or discomfort experienced in the right arm. Mild to severe, it can happen suddenly or gradually. Right arm pain can impact any area of the arm, from the shoulder to the fingertips. Radiating from other body parts, such as the neck or back, is possible. You may experience arm pain if you have shoulder pain.
In contrast, a condition affecting your upper arm may be felt around your shoulder. The main common cause of this type of pain is rotator cuff problems. Left shoulder pain can also be induced by many of these issues. Left shoulder pain may also be caused by organs that cause referred radiating pain.
Common Causes of Right Arm Pain and Warning Signs
There are several probable causes of right arm pain. Understanding the possible causes of right arm pain helps you determine when rest is sufficient and when professional care is necessary.
Common Causes of Right Arm Pain and When to Seek Medical Help
| Cause | Typical Symptoms | When to Seek Help |
|---|---|---|
| Injury or overuse | Swelling, stiffness, pain after activity | If pain persists or movement is limited |
| Pinched nerve | Tingling, burning, or numbness down the arm | Yes — needs medical assessment |
| Poor circulation (PAD, Raynaud’s) | Cold, pale fingers or arm pain when raised | Yes — see a doctor |
| Bursitis or tendonitis | Shoulder or elbow pain, worse at night | If pain continues after rest |
| Peripheral neuropathy | Burning or pins-and-needles sensation | Yes — may need nerve testing |
| Cervical stenosis | Neck pain with arm weakness or numbness | Yes — requires imaging |
| Angina | Chest pressure with arm pain during activity | Urgent — may signal heart disease |
| Heart attack | Chest pain, breathlessness, sweating, nausea | Call emergency services immediately |
| Autoimmune or arthritis | Chronic stiffness, swelling, fatigue | Yes — discuss long-term treatment |
Injury
Injury is one of the most common causes of right arm pain. Trauma to the arm, such as fractures, dislocations, sprains, and strains, can cause pain.
Injuries to the right arm are commonly caused by accidents or falls; overuse injuries can also cause pain. Repeated use of the same muscle group without rest can cause these injuries. Overuse injuries such as tennis elbow and golfer's elbow can cause right arm pain.
Circulation Problems
Circulation problems can also cause right arm pain. A restricted blood flow to your arm can cause tingling, numbness, and pain. Elevating your arm often makes this type of pain worse. Peripheral artery disease (PAD), thrombophlebitis, and Raynaud's disease can cause arm circulation problems.
The arteries that deliver blood to your arms and legs become narrow or blocked when you have PAD. Thrombophlebitis causes inflammation and clotting of the veins. A condition known as Raynaud's syndrome affects blood circulation, causing the fingers and toes to feel cold and numb. Both arms will be affected by many of these conditions.
Peripheral Neuropathy
Nerves that carry messages to and from the brain are damaged in this condition. Diabetes, medications, alcoholism, and vitamin deficiencies may cause peripheral neuropathy.
The symptoms of peripheral neuropathy include numbness, tingling, and pain.
Angina
Angina is a sign of coronary heart disease and means your heart muscles aren't getting enough oxygen-rich blood. Angina causes symptoms like a heart attack, but usually lasts only a few minutes. It typically gets worse when you're active and better when you rest.
Heart Attack
A blood clot or rupture can stop blood flow to a part of your heart in a coronary artery.
As a result, the muscle can become damaged very quickly. The heart muscle begins to die without treatment, which can be fatal. People who are experiencing symptoms of a heart attack should be seen urgently for further evaluation and treatment.
The following symptoms characterise heart attacks:
- Pain or pressure in the chest
- Back, neck, shoulder, or jaw pain
- Vomiting or nausea
- Breathing difficulties
- Fainting or light-headedness
- Sweating profusely
- Tiredness
Cervical Stenosis
A narrowing of the spinal canal causes cervical stenosis. Either arm can experience pain, numbness, or tingling as a result. Physical therapy and medication can often be used to treat cervical stenosis, which is usually caused by arthritis or degeneration of the spine.
Bursitis
The bursa is a fluid-filled sac between a joint's bones and moving parts. Bursitis occurs when the bursa becomes inflamed. Repeated movements often lead to shoulder bursitis. Age increases the risk of bursitis. If you move or lie down on your arm or shoulder, the pain usually increases, and you may be unable to rotate your shoulder fully.
Pinched Nerve
An inflamed or compressed nerve is called a pinched nerve. An injury, a muscle spasm, or a herniated disc can cause it. Your arm may feel numb, tingly, or burning if you have a pinched nerve. When you move, you may feel more pain.
Autoimmune Conditions
Certain autoimmune conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, can cause pain in the right arm, joint, and muscle. The inflammation caused by rheumatoid arthritis affects the joints, whereas the inflammation caused by lupus affects the joints, skin, kidneys, heart, lungs, and blood vessels.
How Doctors Diagnose Right Arm Pain
Based on a person's medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests, a healthcare provider can often diagnose the cause of right arm pain. X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are available imaging tests.
Healthcare providers may recommend blood tests to check for signs of infection or inflammation if the cause of right arm pain is unclear. They may also recommend electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies to diagnose nerve problems.
Effective Treatments for Right Arm Pain
Right arm pain can be treated at home and with medical care.
Home Remedies
Right arm pain can be relieved with several home remedies.
Among them are:
- Heat or ice can be applied to the affected area.
- Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers, including ibuprofen or acetaminophen
- Arm resting
- Keeping away from activities that aggravate the pain
- Posture maintenance
- Lifting weights with proper form
- Hydration
- A gentle exercise program can maintain flexibility and strength, depending on the condition.
Medical Care
Treatment can begin as soon as the cause of right arm pain is identified. Symptoms and underlying causes will be addressed during treatment.
Among them are:
- The immobilisation of your shoulder or arm may help it heal. A sling, brace, or cast is often used to achieve this. When the device can be removed, your medical provider will let you know.
- Corticosteroid injections: A medical specialist can administer this medication to reduce inflammation in inflamed joints.
- In cases of severe pain, prescription pain medications may be prescribed. Certain conditions can be treated with oral corticosteroids to ease inflammation. Treatment options will be discussed with your provider if you have RA or an autoimmune disease.
- Exercise can help you regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion through physical therapy. Physical therapists may be recommended in some cases.
- Surgery may be recommended when other treatments haven't worked or if the damage is severe. Depending on the cause of your condition, a specific procedure may be used.
How to Prevent Right Arm Pain and Injury
You can prevent right arm pain by doing several things.
Here are some good tips:
- Keeping a good posture
- Lifting heavy objects with proper form
- Hydration
- Keeping away from activities that aggravate the pain
- When your arm is sore, rest it.
- Maintaining a healthy physical fitness level
When to See a Doctor for Right Arm Pain
You should seek emergency treatment if you experience severe arm, shoulder, elbow, or wrist pain. If your arm is weak, numb, or broken, call 911 or proceed to the emergency room.
Rarely, right arm pain that worsens with exertion and improves with rest can be a sign of heart disease if it is accompanied by sweating, dizziness, nausea, shortness of breath, jaw pain, or chest pain. Seek medical attention as soon as possible.
How Mobi Doctor Can Help with Arm Pain
Mobi Doctor offers online urgent care. In minutes, you can check your symptoms, research conditions and treatments, and text a healthcare provider if needed.
Mobi Doctor is a virtual clinic that provides online consultations and 24/7 support for people with health problems. You can talk to our experts about any health problem, whether an infection, an injury, or a mental health issue. We offer tailored advice and support from our team of doctors and experts.