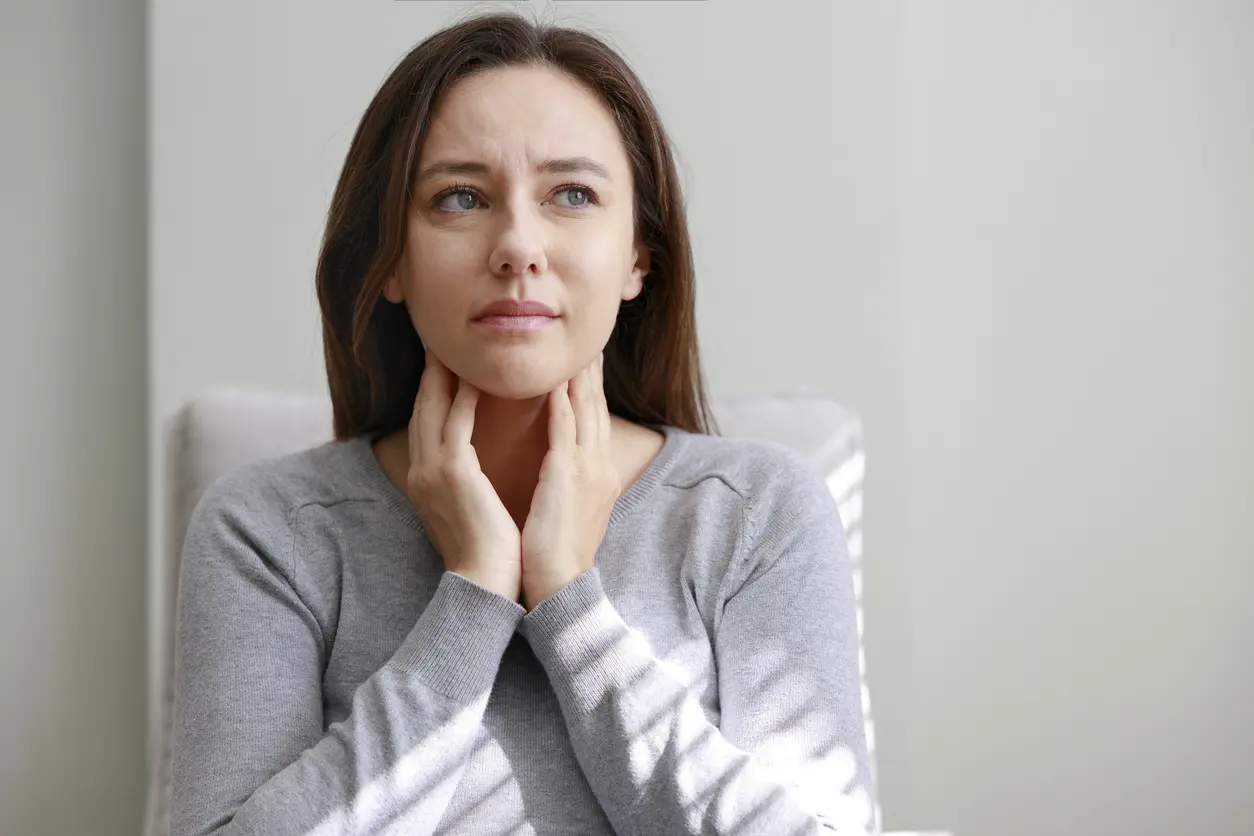
Why do I feel a lump in my throat?
A lump in the throat, or Globus sensation, is often caused by stress, acid reflux, or throat muscle issues. It's usually harmless but can occasionally indicate more serious conditions like thyroid disease or cancer.
Lump In Throat: Possible Causes And Treatment
Have you ever felt something stuck in your throat and wouldn't leave? It's called a Globus sensation when you feel that uncomfortable feeling.
It is also known as Globus pharyngeus or Globus syndrome and can cause distracting and sometimes persistent symptoms. In most cases, a lump in the throat is nothing to worry about.
The likelihood of experiencing this increases with age, with 46% of healthy individuals reporting it at some point. Various conditions can cause a lump in the throat, ranging from psychological stress to cancer. Here are the common and uncommon causes, standard treatments, and prevention methods discussed in this article. A medical professional should also be contacted when necessary.
What Causes a Lump in the Throat?
A lump in the throat was first associated with hysteria in women around 486 BCE by Hippocrates, who called it "Globus hystericus."
This refers to the sensation of having a ball in your throat, as Globus is Latin for "ball."
Although women are more likely to seek medical attention for the condition nowadays, people of all genders can also experience it. Several factors can cause globus syndrome; some are more severe than others. The following list is some of the more common and severe causes of Globus.
Common Reasons for Feeling a Lump in Your Throat
The most common causes of globus syndrome are listed below. Some of these can be easily diagnosed, while others have a more complex diagnosis, even if they aren't severe. To pinpoint the root cause of the globus, a physician must use a process of elimination.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease:
In cases of Globus sensation, doctors look for this first. There has been a link between globus syndrome and abnormal acid pH levels in the throat. Gastric contents directly irritating the laryngopharynx and abnormal vasovagal reflex tightness are two potential explanations for this association.
Esophageal Movement Disorders:
Another leading cause of globus is oesophagal muscle disorders. Esophageal movement disorders account for up to 90% of global cases. After treatment for the motor disorder, the globus feeling disappears.
Pharyngeal Inflammation:
Globus can be caused by irritation or inflammation of the pharynx. Chronic sinusitis with post-nasal drip, pharyngitis, and tonsillitis are some examples.
Hypertrophy Of The Tongue Base:
To determine the cause of globus, it is essential to consider hypertrophy or enlargement of the tongue base.
Abnormal Upper Esophageal Sphincter (UES) Function:
Patients reporting globus sensations are often diagnosed with poor or abnormal UES function. Up to 28% of those with Globus have a history of hypertensive UES in this area of the throat.
Psychological Stress And Other Psychological Factors:
There is an association between Globus sensations, psychological distress, neuroticism, and an introverted personality type. Depression, anxiety, somatic complaints, and environmental stress have also been associated with Globus.
Serious Conditions That May Cause Globus Sensation
Thyroid problems or rare tumours can cause globus pharyngeus as well.
Rare Laryngopharyngeal Tumours:
A lesion or tumour in the throat may be diagnosed later in patients reporting symptoms of globus. One case study describes a patient whose symptoms were misinterpreted as psychological, and the patient's diagnosis was delayed. The endoscopy revealed a muscle tumour in the pharynx, emphasising the need for a complete examination.
Pharyngeal Cancer:
A globus sensation may be experienced due to nasal congestion and neck swelling caused by pharyngeal cancer. A lump may appear on the upper part of the neck, but it is not painful. Pharyngeal cancer has no known cause but can be diagnosed by an endoscopy, which is also part of the diagnosis process. Malignant tumours and cancer are also diagnosed by biopsying the affected cells.
Thyroid Diseases:
According to one study, early were reported by up to a third of patients undergoing thyroid surgery globus symptom. The globus sign was also reported to be gone in 80% of patients after their operation. Because thyroid issues can cause many symptoms, they often go undetected or misdiagnosed. To be safe, thyroid problems should be ruled out when diagnosing the globus.
How to Tell If a Throat Lump Is Serious
Occasionally, lumps in the throat are nothing more than abnormal sensations. Many common and severe symptoms look the same, making it hard to distinguish between them. A medical professional will use a process of elimination to get an accurate diagnosis and treatment. As well as Globus, gastroesophageal reflux disease tends to cause heartburn, regurgitation, and belching.
Common vs. Serious Causes of Lump in Throat
| Cause Type | Example Conditions | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Common | Acid reflux, throat inflammation, stress | Usually harmless |
| Psychological | Anxiety, depression, stress-related Globus | Often manageable |
| Structural | Enlarged tongue base, UES dysfunction | Varies |
| Serious | Thyroid disorders, pharyngeal cancer | Requires care |
Treatment Options for Globus Sensation
When Globus sensations arise for non-serious reasons, there are many possible treatments. Depending on the underlying cause, your doctor may choose one of these options. It is often necessary to perform a nasolaryngoscopy or another endoscopy exam to determine the cause of the problem. During an endoscopy, your doctor passes a special camera down your nose or throat to inspect your voice box and throat. For further examination, a tissue biopsy in the area may be taken. Usually, gastroesophageal reflux disease causes globus sensations, which can be diagnosed through a medical examination. The treatment can begin immediately after the diagnosis has been made.
In this case, Lansoprazole, a proton pump inhibitor, is given to the patient at a high dose. After eight weeks of treatment with this medication, 80% of patients report that their symptoms of globus are "dramatically improved." When someone has trouble swallowing, they are diagnosed with oesophagal movement disorders, also known as oesophagal motility disorders.
Pharynx, tongue, and esophagus all need to function correctly to swallow. Treating throat problems with medications that either reduce or increase muscle activity, depending on which organ isn't functioning well, is possible.
Psychological treatment is sometimes included in treatment. Esophageal motor disorders include abnormal upper esophageal sphincter (UES) function.
As part of the treatment plan, laryngitis and paropharyngitis may require voice rest, steam inhalation, avoiding irritants like alcohol or smoking, and dietary changes.
Supportive care will help your body fight an infection caused by a viral upper respiratory tract infection.
Speech therapy and/or language therapy may be used in treating psychological factors associated with globus.
Patients experiencing psychological distress that exacerbates the globus sensation may also benefit from reassuring them that their health is good.
How to Prevent a Lump in the Throat Feeling
Staying hydrated and eating well is vital to preventing distracting throat sensations.
The best way to maintain a healthy throat is to refrain from activities that may irritate or aggravate it, such as:
- Consuming caffeine
- Smoking
- Drinking alcohol
Drink cold or carbonated water instead of coughing or clearing your throat if you occasionally experience Globus symptoms.
How Common Is the Lump in Throat Sensation?
Approximately 46% of otherwise healthy individuals report experiencing globus sensations.
Most people with globus sensations (up to 45%) report still experiencing them after a follow-up survey.
When Should You Worry About a Lump in Your Throat?
Multiple organs reside in your throat, which helps you eat, drink, swallow, speak, and breathe.
A medical professional should be consulted if you experience a lump in your throat that does not disappear after the time it usually takes to recover from a cold.
Schedule an appointment with your doctor if you are experiencing the following symptoms along with the Globus sensation.
More serious concerns, such as cancer, can be indicated by these symptoms:
- Difficulty swallowing
- Throat pain
- Pain when speaking
- Changes to your voice
- Unexplained weight loss
- Pain while swallowing
- Enlarged lymph nodes or other lumps in the neck
Frequently Asked Questions About Lump in Throat
Why does my throat feel like it has a lump?
This could be due to acid reflux, muscle tension, or psychological stress. It’s called Globus sensation and is usually harmless.
Can anxiety cause a lump in the throat?
Yes. Psychological stress and anxiety are common triggers for Globus sensation and can make symptoms feel more intense.
How do I get rid of the lump in my throat feeling?
Staying hydrated, managing stress, and treating any underlying reflux or inflammation can help. Medical advice is recommended for persistent symptoms.
Is the lump in my throat dangerous?
Not usually. However, symptoms like difficulty swallowing, voice changes, or weight loss should be checked by a doctor.
When should I see a doctor about a throat lump?
If the sensation persists for more than a few weeks or comes with pain, weight loss, or visible swelling in the neck, seek medical advice.
How Mobi Doctor Can Help
Mobi Doctor offers online urgent care. In minutes, you can check your symptoms, research conditions and treatments, and text a healthcare provider if needed.
Mobi Doctor is a virtual clinic that provides online consultations and 24/7 support for people with health problems. You can talk to our experts about any health problem, whether an infection, an injury, or a mental health issue. We offer tailored advice and support from our team of doctors and experts.