Spotting STIs And STDs: Identifying Them And Lowering Infection Chances
We don't often talk about STIs (sexually transmitted infections) or STDs (sexually transmitted diseases. People usually feel ashamed or embarrassed about them. And because not many people know about them, many wrong ideas go around.
We want to break the shame around sexual health and STIs. We'll share helpful information to help you know the signs of infection and lower the chance of infection. We'll also check out how STIs are treated and how testing works. Let's begin!
The Difference Between STIs And STDs
Before discussing different types of infections that spread through sex and their signs, let's clear up a myth – STIs and STDs aren't the same. Even though people often use the words interchangeably, they're not exactly alike. Infection happens when viruses or bacteria get inside the body and start growing.
Viruses and bacteria that spread through sex can move from one person to another by touching skin, like during physical contact. They can also pass through sharing bodily fluids, such as sperm, vaginal fluids, or blood.
STIs are often sneaky because they don't show symptoms – you might not feel anything. But you'll notice signs of trouble when the infection worsens and hurts your cells. That's when we call it a sexually transmitted disease. So, diseases start as infections in the beginning!
How Do I Know If I Have An STI? What Are The Most Common Infections?
Chlamydia is the most common infection that spreads through sex. But there are also other common infections like gonorrhoea, syphilis, and genital herpes. The Health Protection Surveillance Centre found that some infections, including HIV, have increased significantly compared to last year (2021). This might be because the COVID-19 rules are not as strict now, and we are returning to our everyday social lives. Even though things are getting better, it's still essential to take care of your sexual health to lower the chances of getting these infections.
Here's what you need to know about some of the most common STIs.
Chlamydia
In Ireland, the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI) is chlamydia. This is especially true for people who are 35 years old or younger. This infection can stay in your private parts, mouth, and bottom. So, if you have sex with someone who has it, whether it's vaginal, anal, or oral, you can get it too. Most of the time, people who have chlamydia don't feel any signs that they're sick. About 70% of girls and 50% of boys don't have any symptoms!
You might feel pain when peeing in your tummy or lower part if you feel something wrong. For girls, sex might hurt, and they could have weird stuff coming out down there, bleeding after sex or between their periods. For boys, there might be watery or white stuff from their private parts, pain in their balls, and it might burn or itch when they pee. Chlamydia can also make your eyes red and irritated, like pink eye.
If you don't get help for chlamydia, it can make you sick, especially if you're a girl. It might lead to problems like hurting your belly and making it hard to have babies later. It could even damage the tubes where babies grow, making it dangerous if they start growing in the wrong place. For boys, it can hurt their private parts and make it tough to have babies too. So, it's essential to treat it!
Fortunately, chlamydia is typically responsive to antibiotics, and you can initiate treatment once an STI test confirms the presence of the infection. If you notice any symptoms of chlamydia, it's advisable to visit a sexual health or genitourinary medicine (GUM) clinic or consult your general practitioner (GP) without delay. Starting treatment as early as possible offers better outcomes.
Chlamydia can often go unnoticed by many individuals. That's why it's valuable to undergo regular testing. This practice not only aids in avoiding the accidental transmission of the infection but also ensures prompt access to treatment if necessary.
Gonorrhoea
Gonorrhea is a bacterial infection that spreads through sexual activity like vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected partner. Similar to chlamydia, lots of people with gonorrhoea don't feel any symptoms and might not realise they're infected. Surprisingly, 1 out of 10 guys and nearly half of the women don't show any signs at all! That's why it's wise to get tested every time you start a new sexual relationship, and it's a good idea to ask your partner to do the same.
Common signs of gonorrhoea include having thick green or yellow stuff coming out from the private parts and feeling pain when peeing. Girls might also have to bleed between their periods. If gonorrhoea isn't treated, guys can get an infection in their private parts, like the testicles, prostate, and penis. For girls, it can lead to infections in the womb, fallopian tubes, and private parts. This can mess up the ability to have babies for both guys and girls.
If you have gonorrhoea, you can get better with a shot of antibiotics. If you notice any signs of gonorrhoea or a test says you have it, go to your doctor or a sexual health clinic for help.
Syphilis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) that mainly spreads through vaginal, anal, and oral sex. It creates little sores (called ulcers) in the mouth, throat, private parts, anus, or the outside parts like the penis and vulva. Syphilis spreads when one partner touches these sores during sex.
When you first get syphilis (an infection), it happens about 2-3 weeks after you catch it. You might get small sores on your private parts, mouth, anus, or even your hands at that time. These sores don't hurt, so you might not even realize you have them.
If the first (primary infection) isn't treated, a second (secondary infection) can show up in about a month. The symptoms might not be strong and can be hard to notice. They might show up, disappear, or change with time. Some common signs include:
- You could get a rash on your hands and feet. It doesn't usually make you itch and can spread everywhere.
- You might see white patches in your mouth.
- You could feel like you have the flu – things like headaches, high temperature, and tiredness.
- Your glands might swell up.
- You might notice white or grey wart-like growths on your private parts or around your anus.
A third infection can happen many years after the first one and can cause big problems for your nerves, heart, and blood vessels.
Even though syphilis does show signs, it might take 3 weeks or longer for these signs to show up after you catch it. These signs could improve independently, but the infection is still in your body and can spread to partners. That's why it's essential to get tested if you have sex without protection with someone new or if you feel any of the symptoms I mentioned earlier.
A Syphilis Infection Can Cause Severe And Potentially Life-Threatening Health Problems If Left Untreated.
Antibiotics can be used to treat syphilis, but it will depend on the stage of the disease. Early detection and treatment of syphilis are crucial to prevent severe and potentially life-threatening health complications.
Syphilis (tertiary) untreated can lead to:
- Heart problems like chest pain (angina), a weakened aorta (aortic aneurysm), and heart failure.
- Brain problems include seizures, trouble remembering things, changes in your act, and even dementia.
- Nerve problems that might make you feel tingling have joint pain and slowly harm your joints.
Additionally, syphilis can affect bones, testicles, liver, skin, and other organs.
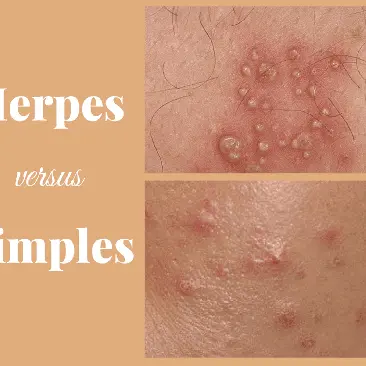
Genital Herpes
Genital herpes is an infection from the herpes simplex virus (HSV), which spreads through kissing, touching private parts, having sex (vaginal, anal), and even oral sex. It's straightforward to catch. You could also get it by sharing sex toys with someone who has it.
Two kinds of HSV can give you genital herpes. HSV Type 1 is the main cause because it can spread from cold sores during oral sex. HSV Type 2 is less common but more likely to cause repeat infections.
When you first get HSV, it's called the "primary infection." Some folks won't feel anything, so they might not realize they have it – we call this a "subclinical infection." But some people might feel sick in general and have stronger symptoms than later times they get it again.
If you're worried about this infection, visit your doctor or a sexual health clinic. They'll check you in person to confirm if you have it. Also, getting tested for other STIs simultaneously is a good idea because they can be there too.
Unfortunately, There Is Currently No Cure For Genital Herpes, But Symptoms Are Manageable
After the first (primary infection), the virus stays quiet in the skin's nerve cells. But it can wake up again at any time and cause repeat episodes. These can make blisters or sores on the butt, thighs, anus, mouth, and private parts. For girls, sores can appear inside or outside the private parts and on the cervix. For guys, they can appear on the tube you pee from, the penis, and the balls. This infection sticks around for life.
How Can I Reduce The Risk Of Getting An STI?
In the case of STIs and STDs, prevention is always better than cure. An STI can be reduced in some simple ways.
1. Use Barrier Methods Of Contraception
To protect yourself, you can use things like condoms for guys and girls and dental dams. These stop direct skin contact and prevent fluids like semen and stuff from the private parts from spreading. This can lower your chances of getting infected.
STIs often go undetected because they don't cause symptoms. Whenever you engage in sexual activity, you should wear barrier protection. Intimate contact and sex can all lead to the transmission of STIs.
So that you know, condoms and similar things only cover the skin on the penis. They can't give total protection but lower the chance of passing things on. This is important for infections like HPV that cause warts and herpes/cold sores. The virus lives on the skin, so these methods can still help.
2. Avoid Sexual Contact If There Is Any Sign Of Infection
Suppose you or your partner exhibit any indications of infection, such as genital sores, blisters, unusual discharge, or bleeding. In that case, it's essential to abstain from any form of sexual activity until both you and your partner have been tested and appropriately treated. In the case of genital herpes, it's advisable to avoid intimate contact until the sores or blisters have fully healed.
3. Avoid Sharing Sex Toys
As previously stated, sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can be transmitted through sex toys. For this reason, we advise against sharing such toys. If you choose to share them, cleaning the toys after each use is essential. Another precautionary measure is to place a new condom on the toy before each use.
4. Get Vaccinated
Vaccines are accessible for certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like hepatitis B. Specific strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV) can lead to genital warts, genital herpes, and certain forms of cancer. Opting for an HPV vaccination can contribute to diminishing the propagation of HPV infections and lowering the likelihood of encountering these health conditions.
5. Regular Testing
As you've learned, lots of people won't feel any signs if they have common STIs. They might not realise they're infected. So, it's super important to get tested often. If you find out early, you can stop them from spreading accidentally and get treatment if needed. Treating STIs early is the best thing to do!
Going to a sexual health clinic might make you a bit nervous, especially if it's your first time. But there's no reason to feel embarrassed or ashamed! The people who work at these clinics won't judge you or say anything mean. They're there to help you and provide support. Many people get STIs – it's quite common, and many will have one at some point in their lives!
It is also possible to check your sexual health from the comfort of your home. If you're uncomfortable with visiting a clinic in person and prefer to have a consultation online, you can contact Mobi Doctor for assistance. Mobi Doctor offers the option of getting medical advice and support through online consultations, allowing you to seek help from the comfort of your own space. This can be particularly helpful if you have questions or concerns about sexual health or other medical matters. Remember, seeking guidance is essential for taking care of your health!